MOTIS v0.8: Basic GBFS Support
With MOTIS version 0.8, we introduce basic support for the GBFS standard. GBFS is used by many providers that offer bike sharing, car sharing or e-scooter sharing.
Supported Journey Patterns
MOTIS supports both station bound as well as free-floating vehicles on the first and last part of the journey. Jounreys can start and/or end with:
- walking to the free-float vehicle and driving it to the destination (stop or final destination)
- walking to the sharing station, driving the vehicle to a sharing station close to the destination, walking to the destination
Routing Approach
The approach makes use of several one-to-many and many-to-many table routing requests to the OSRM router embedded in MOTIS as the osrm module.
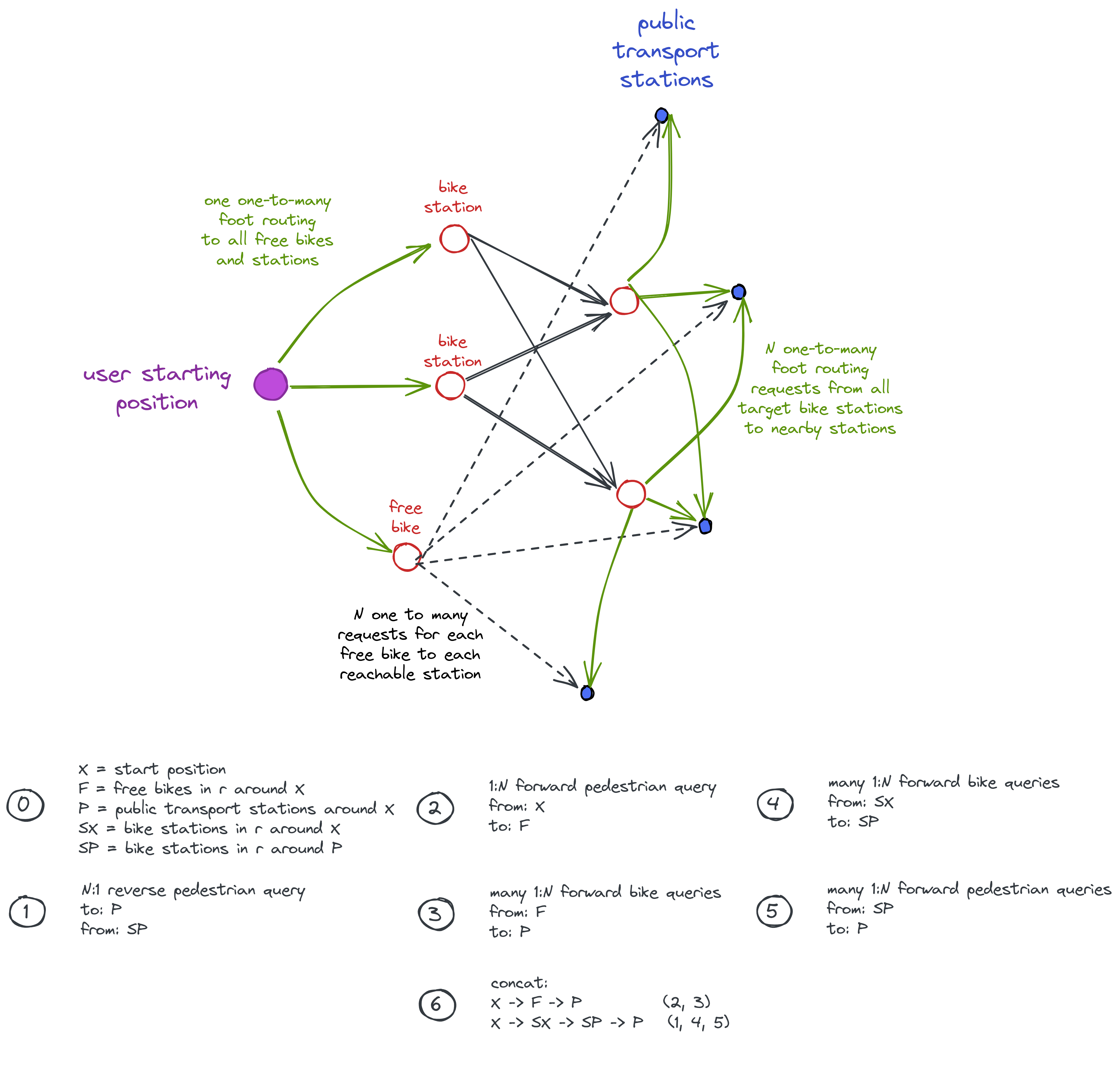
The following sketch illustrates the routing approach. Green arrows indicate walking, solid arrows indicate driving a station vehicle, and dashed arrows represent driving a free-float vehicle. The graphic shows the way all optimal routes from the starting address to nearby public transport stations as well as to the final destination address are computed.
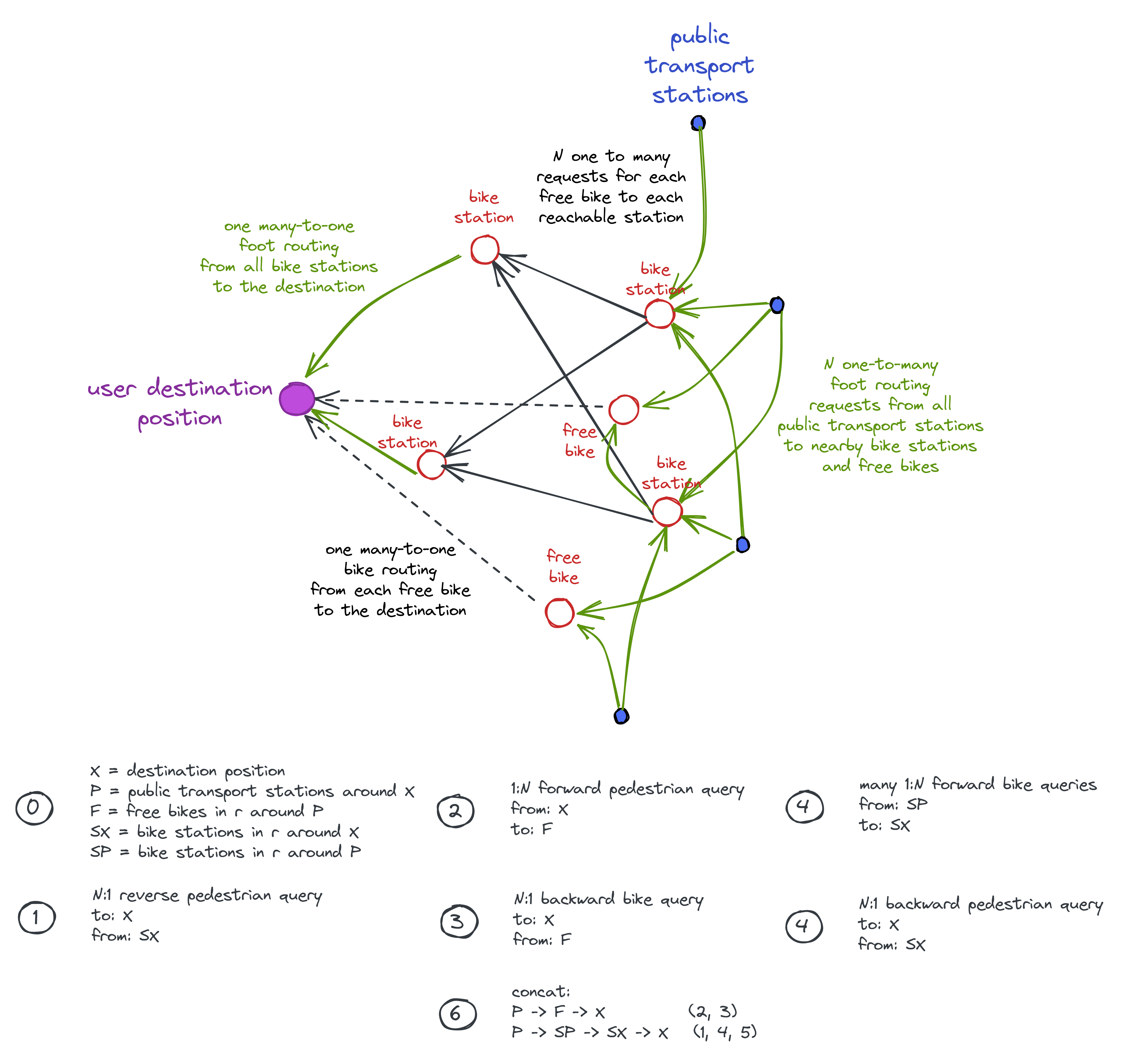
The backward search inverts this. However, it’s not the case that every arrow from the previous picture is just inversed: the free-float vehicles require first walking from the public transport station to the vehicle which is used until the final destination of the user is reached.
Web UI
The menu for choosing transport modes at start and destination address has been extended. In a first step after loading the page, it fetches all supported GBFS providers from the backend. By default these are disabled. They can be enabled and configured by the user.
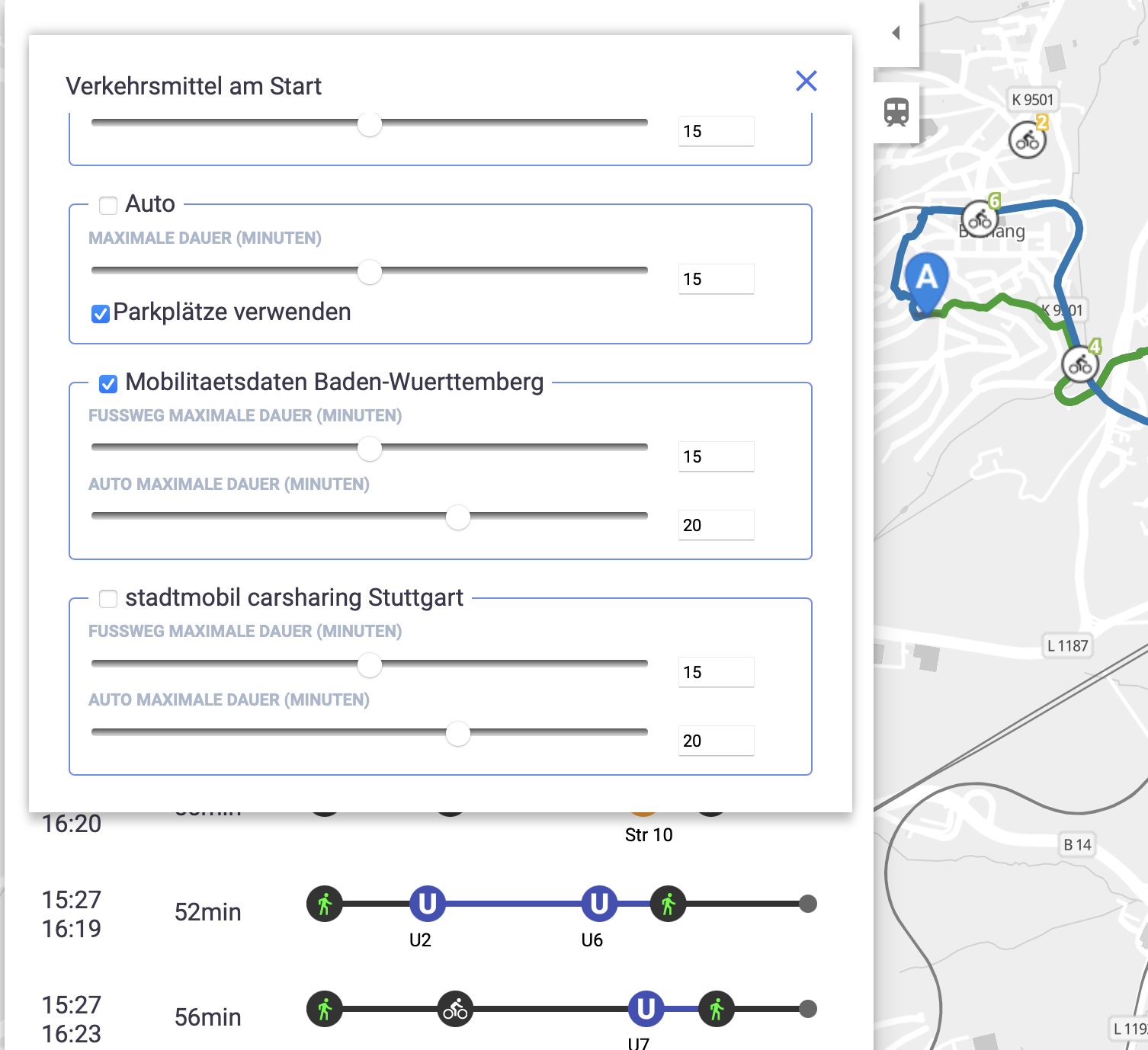
As shown in the screenshot, it’s possible to configure a maximum duration for driving the vehicle as well as for walking.
Info Map
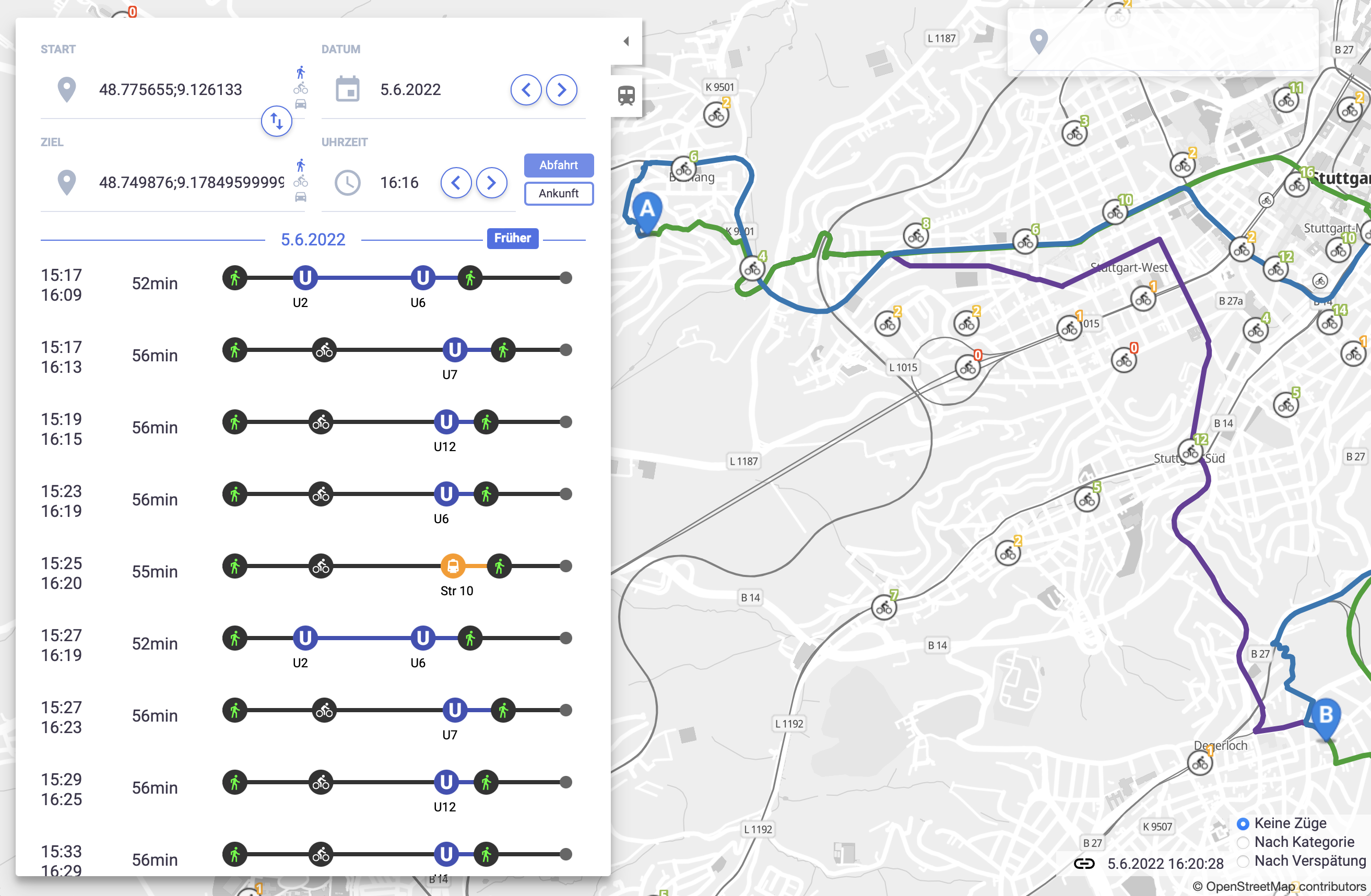
In addition to the routing functionality, the new GBFS module in MOTIS provides vector tiles showing free-float vehicles as well as sharing stations. The station vector tile layer provides also information about the number of available vehicles.
API
Computing Connections
The GBFS module is used by the intermodal module to compute intermodal journeys. It can, however, also be used standalone to compute optimal connections involving only GBFS-based sharing mobility.
The module computes connections to all public transport stations reachable in the specified time limits for walking and driving. Additionally, it is possible to give direct targets that are not public tranport stations as shown in the example request below:
curl -XPOST -H "Content-type: application/json" -d '{
"destination": {
"type": "Module",
"target": "/gbfs/route"
},
"content_type": "GBFSRoutingRequest",
"content": {
"dir": "Forward",
"provider": "stadtmobil",
"x": {
"lat": 48.77541,
"lng": 9.158932
},
"direct": [{"lat":48.7768,"lng":9.2102}],
"max_foot_duration": 10,
"max_bike_duration": 15
}
}' 'https://europe.motis-project.de'
Provider List
The provider list can be requested using a simple HTTP GET request to /gbfs/info. It gives additional info about the provider of the serivce including URL and purchase URL. Every provider has a unique tag provided in the MOTIS config.ini. This tag is required to request the tiles according to this provider.
Tiles API
The vector tiles API endpoint is available under /gbfs/tiles/${tag}/{z}/{x}/{y}.mvt. The tag needs to be read from the provider list API.
Sponsor
This work is sponsored by INIT.